 In today’s energy sector, efficiency isn’t just about how much power a transformer can deliver—it’s about how responsibly we use the resources behind it. Every transformer represents tons of copper, steel, oil, and insulating materials that can be given a second life...
In today’s energy sector, efficiency isn’t just about how much power a transformer can deliver—it’s about how responsibly we use the resources behind it. Every transformer represents tons of copper, steel, oil, and insulating materials that can be given a second life...
 Eco-Friendly Insulating Fluids Traditional mineral oils used in transformers present risks of environmental contamination if leaks occur. To address this, many utilities and manufacturers are adopting biodegradable insulating fluids, such as natural esters derived...
Eco-Friendly Insulating Fluids Traditional mineral oils used in transformers present risks of environmental contamination if leaks occur. To address this, many utilities and manufacturers are adopting biodegradable insulating fluids, such as natural esters derived...
 What Is Life Cycle Cost? Life cycle cost refers to the total cost of owning and operating a transformer throughout its service life. This includes: Acquisition cost – purchase price, shipping, and installation. Operating cost – primarily energy losses (no-load and...
What Is Life Cycle Cost? Life cycle cost refers to the total cost of owning and operating a transformer throughout its service life. This includes: Acquisition cost – purchase price, shipping, and installation. Operating cost – primarily energy losses (no-load and...
 The Growth of Renewable Energy in the U.S. In states like California, Texas, and Nevada, solar farms are expanding rapidly, while wind power is booming in regions such as Iowa, Oklahoma, and along the Atlantic coast. Together, solar and wind account for a growing...
The Growth of Renewable Energy in the U.S. In states like California, Texas, and Nevada, solar farms are expanding rapidly, while wind power is booming in regions such as Iowa, Oklahoma, and along the Atlantic coast. Together, solar and wind account for a growing...
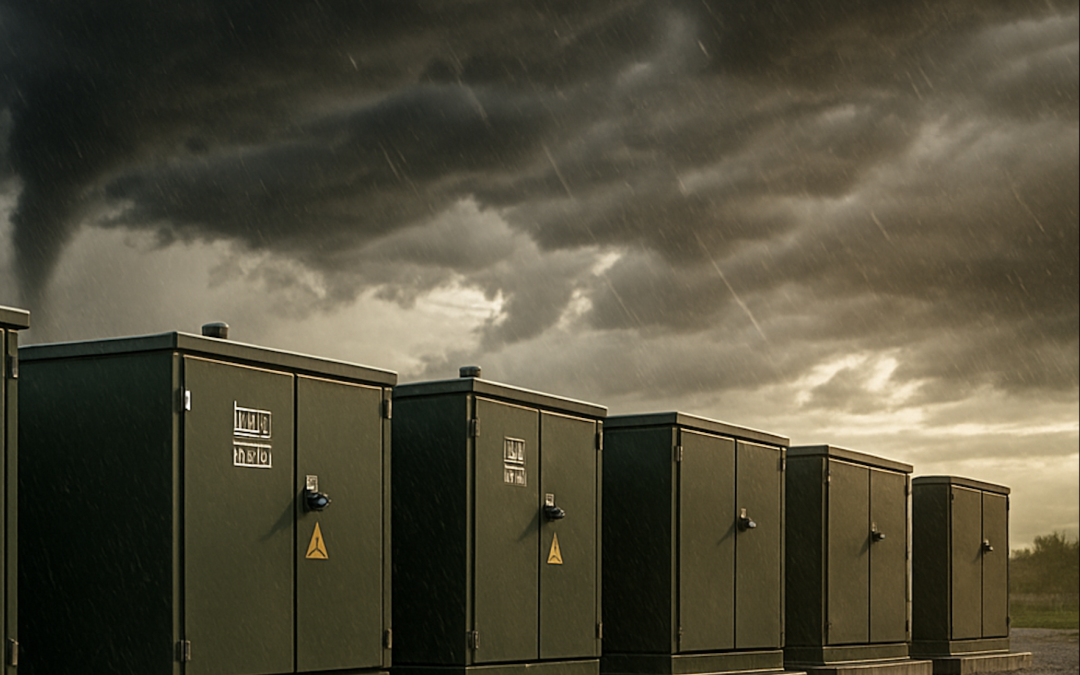 Even glancing blows test grid weak points. Salt-fog, wind-borne debris, storm surge, and sheet flooding attack enclosures, bushings, and mounting hardware; thermal cycling and contamination accelerate wear. U.S. Department of Energy guidance on transformer resilience...
Even glancing blows test grid weak points. Salt-fog, wind-borne debris, storm surge, and sheet flooding attack enclosures, bushings, and mounting hardware; thermal cycling and contamination accelerate wear. U.S. Department of Energy guidance on transformer resilience...
 Electrical transformers are often seen as just another piece of industrial equipment but behind their metallic frames lies a fascinating history of innovation, physics, and engineering. From their invention in the 19th century to their essential role in today’s energy...
Electrical transformers are often seen as just another piece of industrial equipment but behind their metallic frames lies a fascinating history of innovation, physics, and engineering. From their invention in the 19th century to their essential role in today’s energy...







